Welcome to Sukyoung K. Yi's group (GEM) homepage!
이석영 교수의 은하진화 연구 그룹 홈페이지에 오신것을 환영합니다.

Science Goal 연구 목표
We aim to understand the formation and evolution of galaxies. 우리 그룹의 연구 목표는 은하의 형성과 진화과정을 이해하는 것입니다.
News 소식
- GEM-KASI Hector workshop will be held on 27 January, 2026 in Yonsei University, Seoul, Korea
- 2025 NewCluster Workshop@IAP will be held on 2 - 8 July, 2025 in Paris, France
- The 2025 NewCluster data workshop will be held on 18 - 21 February, 2025 in Jeonju, Korea
- Dr. Scott Croom and Dr. Garreth Martin will visit GEM (14-25 Oct 2024)
- The 2024 NewCluster workshop will be held on 26 - 30 August, 2024 in Yonsei university, Seoul, and Gangneung, Korea
- The 2023 GEM Fall workshop will be held on 20 - 21 October, 2023 in Ramada hotel, Jeju, Korea
- The 2022 GEM Winter workshop will be held on 8 - 11 January, 2023 in WE hotel, Jeju, Korea
- The 2020 GEM 2nd workshop will be held on 19 - 21 August, 2020 in Yonsei University, Seoul, Korea (Cancelled)
- The 2020 GEM workshop will be held on 14 - 17 January, 2020 in Gyeongju, Korea
- Minjung Park's paper has been introduced by AAS Nova (23 September 2019).
- Dr. Sandro Tacchella will visit GEM (8-11 July, 2019)
- The 2019 GEM - CASCADE workshop will be held on 1 - 4 July, 2019 in Jeju, Korea
- The 2018 GEM workshop will be held on 2 - 4 July, 2018 in Kangnung, Korea
- Dr. Scott Croom, Dr. Julia Bryant and Dr. Warrick Couch will visit GEM (10-13 Apr 2017)
- Dr. Barbara Cantinella and Dr. Luca Cortese at ICRAR are visiting GEM (1-15 Apr 2017)
- SAMI workshop will be held at KASI. (12 Apr 2017)
- Environment workshop wiil be held. (3 Apr 2017)
Recent Paper 최근 논문
How dust models shape high-z galaxy morphology: Insights from the NewCluster simulation
Gyeong-Hwan Byun, J. K. Jang, Zachary P. Scofield, Eunmo Ahn, Maarten Baes, Yohan Dubois, San Han, Seyoung Jeon, Juhan Kim, Christophe Pichon, Jinsu Rhee, Francisco Rodríguez Montero, and Sukyoung K. Yi
 |
Summary
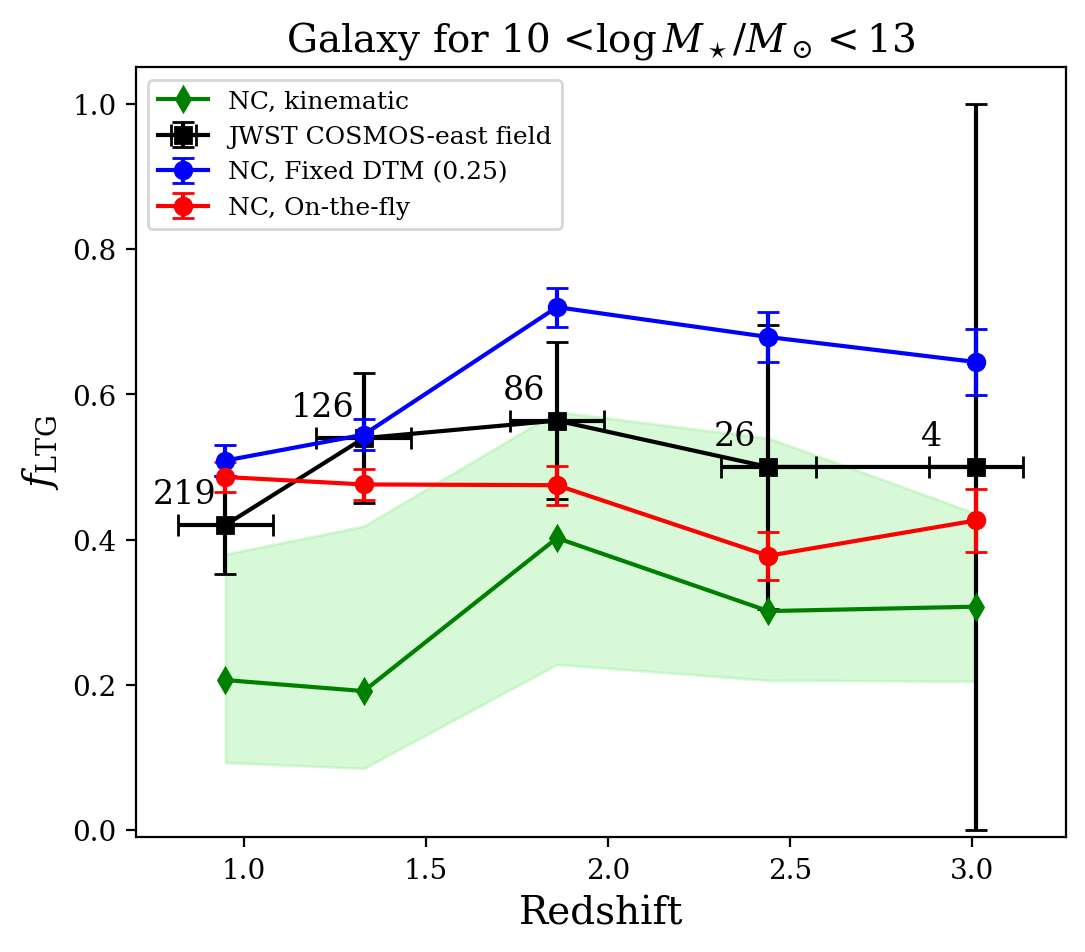
Dust plays a pivotal role in shaping the observed morphology of galaxies. While traditional cosmological simulations often assume a fixed dust-to-gas (DTG) or dust-to-metal (DTM) mass ratio to model dust effects, recent advancements have enabled on-the-fly (OTF) dust modeling that captures the spatial and temporal evolution of dust. In this work, we investigate the impact of dust modeling on galaxy morphology using the NewCluster simulation, which implements a detailed OTF dust model. We generate mock images of NewCluster galaxies under both OTF and fixed DTM models using the radiative transfer code SKIRT, and compare their morphology to JWST observations. We measure morphology indices and use the \gm\ test to classify galaxies. We find that the OTF galaxy models exhibit brighter centers and more pronounced bulges than those of the fixed DTM models, resulting in a lower late-type galaxy (LTG) fraction, particularly at high redshifts. This central brightening is linked to a phenomenon we refer to as the DTM cavity, a localized depression in the DTM ratio driven by intense bulge starbursts. Our results highlight the importance of modeling dust evolution in a physically motivated manner, as fixed DTM models fail to capture key morphological features.
국문 요약
기존 우주론적 시뮬레이션에서는 고정된 먼지-금속 비율(DTM)을 가정해 먼지를 모델링해 왔으나, 최근에는 먼지의 시공간적 진화를 직접 추적하는 실시간(on-the-fly, OTF) 먼지 모델이 도입되고 있다. 본 연구에서는 OTF 먼지 모델을 구현한 NewCluster 시뮬레이션을 사용하여, 먼지 모델링 방식이 은하 형태에 미치는 영향을 분석하였다. OTF 모델과 고정 DTM 모델에 대해 복사전달 코드 SKIRT로 모의 관측을 하고, JWST 관측과 비교하였다. 또한 형태 지수와 G-M_20 분류를 이용해 은하 형태를 정량적으로 분석하였다. 그 결과, OTF 모델을 적용한 은하들은 고정 DTM 모델에 비해 중심부가 더 밝고 팽대부가 더 두드러지며, 특히 높은 적색편이에서 후기형 은하의 비율이 감소하는 경향을 보였다. 이러한 차이는 강한 중심부 별탄생에 의해 형성된 국소적인 DTM 감소 영역(‘DTM cavity’)과 관련이 있다. 본 연구는 은하 형태 연구에서 물리적으로 일관된 먼지 진화 모델링의 중요성을 보여준다.